今年RL的论文怎么这么多。。。
Key words
- RL $\times$ Adersarial learning
- Guided-policy search (Model-based RL)
- GAIL (IRL)
- Multi-agent RL
- Soft Q-learning (PGM)
Adversarial learning
Excessive Invariance Causes Adversarial Vulnerability
只看标题觉得结论还是比较有趣的,先mark一下
The Limitations of Adversarial Training and the Blind-Spot Attack
文章研究了adversarial training中存在的blind-spot现象,作者在abstract中如此解释blind-spot attack:
Consequentially, an adversarial training based defense is susceptible to a new class of attacks, the “blind-spot attack”, where the input images reside in “blind-spots” (low density regions) of the empirical distri- bution of training data but is still on the ground-truth data manifold.
The existence of blind-spots in adversarial training makes defending on any valid test examples difficult due to the curse of dimensionality and the scarcity of training data.
此外作者还发现了2018年Kolter & Wong以及Sinha et al.的adversarial training方法都存在blind-spot问题
Reinforcement learning
Variational Discriminator Bottleneck: Improving Imitation Learning, Inverse RL, and GANs by Constraining Information Flow
- UCB大佬集团出品,Pieter Abbeel和Sergey Levine都在作者名单里,
- Variational information bottleneck并非首创,早在2016年Alemi et al.的工作就已经将其用于supervised learning任务,以此来reduce model variance;相比之下本文的创新在于将这种思路拓展至几个经典的需要使用discriminator/critic的场景:
- GAN生成图像,unsupervised learning,文章后面的实验中放了几张生成的$1024\times{}1024$的人脸大图
- GAIL,第一篇为基于GAN做imitation learning提供理论基础的文章
- AIRL,将GAIL拓展至inverse RL的工作
- 直接constraint mutual information的upper bound,训练时用了截断的dual gradient descent,此外实验一节也提出了若干trick (加GP等),目测复现比较困难
Temporal Difference Variational Auto-Encoder
Motivation很有说服力,作者认为一个agent的experience modeling应该具有三个性质:
- model应当学习到MDP中state空间的抽象表示,而不仅仅局限于根据observation做判断
- model应当学习belief state
- mode应当能够学习到时域上的抽象,从而使得agent的planning可以更长远
Rigorous Agent Evaluation: An Adversarial Approach to Uncover Catastrophic Failures
选题很新潮,Motivation是在safety-critical场景下evaluate agent,审稿人的summary简洁而准确:
Proposes an importance sampling approach to sampling failure cases for RL algorithms. The proposal distribution is based on a function learned via a neural network on failures that occur during agent training. The method is compared to random sampling on two problems where the “true” failure probability can be approximated through random sampling. The IS method requires substantially fewer samples to produce failure cases and to estimate the failure probability.
此外也是用adversarial learning的思路来做RL,可以看出这种思路将成为一种大的趋势
Woulda, Coulda, Shoulda: Counterfactually-Guided Policy Search
Guided policy search系列的工作,需要稍微查一下之前的文献才能看懂
CEM-RL: Combining evolutionary and gradient-based methods for policy search
In this paper, we propose a different combination scheme using the simple cross-entropy
method (CEM) and Twin Delayed Deep Deterministic policy gradient (TD3), another off-policy deep RL algorithm which improves over DDPG.
审稿人1的评论
This paper combines two different types of existing optimization methods, CEM/CMA-ES and DDPG/TD3, for policy optimization. The approach resembles ERL but demonstrates good better performance on a variety of continuous control benchmarks. Although I feel the novelty of the paper is limited, the provided promising results may justify the acceptance of the paper.
Directed-Info GAIL: Learning Hierarchical Policies from Unsegmented Demonstrations using Directed Information
Imitation learning领域的新鲜血液,2017年NIPS上info-GAIL的延伸
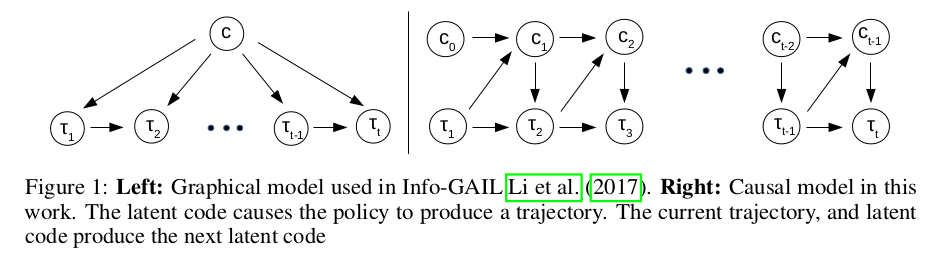
- 解决的问题:
- Learning a macro-policy from unsegmented expert demonstrations
- Unsupervised inference of subtask-specific latent variables
- 提出的方法
- 将info-GAIL的PGM推广为sequence of latent variable的形式,优化latent variable与state-action pair的directed mutual information
- 采用Gumbel trick来解决latent variable离散的问题
- 用expert demonstrations预训练了一个VAE用于从latent variable的先验分布中采样
- 作者分析了提出的方法与options framework的关联
- 实验中有若干离散latent variable可视化的例子,作者以此来证明他们方法中latent variable的interpretability,审稿人认为实验比较弱,没有大型continuous control任务上的evaluation
- 个人认为与infoGAN的inference相似,由于复杂任务的subtask表示本身具有某种程度的复杂性,这种inference很难在复杂任务上学习到对人类有意义的latent variable representation
Hindsight policy gradients
Jürgen Schmidhuber出现在了通讯作者的位置上,审稿人认为contribution有限,但AC力排众议给了这篇文章很高的评价
Metareview:
The paper generalizes the concept of “hindsight”, i.e. the recycling of data from trajectories in a goal-based system based on the goal state actually achieved, to policy gradient methods.
Review 1:
The authors present HPG, which applies the hindsight formulation already applied to off-policy RL algorithms (hindsight experience replay, HER, Andrychowicz et al., 2017) to policy gradients.
Probabilistic Planning with Sequential Monte Carlo methods
Sequential Monte Carlo (SMC) has since its inception some 25 years ago proved to be a powerful and generally applicable tool. The authors of this paper continue this development in a very interesting and natural way by showing how SMC can be used to solve challenging planning problems. This is a enabled by reformulating the planning problem as an inference problem via the recent trend referred to as “control as inference”.
Learning to Understand Goal Specifications by Modelling Reward
文章讨论了NLP任务中的RL应用,当reward没有良好定义的时候,如何用一个discriminator D来生成pseudo rewards。感觉motivation蛮有趣的,可以一读。
Adversarial Imitation via Variational Inverse Reinforcement Learning
Metareview给了这篇文章很高的评价
作者在abstract中claim的contribution:
Our proposed method builds on the framework of generative adversarial networks and introduces the empowerment-regularized maximum-entropy inverse reinforcement learning to learn near-optimal rewards and policies. Empowerment-based regularization prevents the policy from overfitting to expert demonstrations, which advantageously leads to more generalized behaviors that result in learning near-optimal rewards.
Reviewer在评论区claim的contribution:
This paper builds on the AIRL framework (Fu et al., 2017) by combining the empowerment maximization objective for optimizing both the policy and reward function. Algorithmically, the main difference is that this introduces the need to optimize a inverse model (q), an empowerment function (Phi) and alters the AIRL updates to the reward function and policy. This paper presents experiments on the original set of AIRL tasks, and shows improved performance on some tasks.
The Laplacian in RL: Learning Representations with Efficient Approximations
Abstract非常吸引我,感觉讨论的问题很有趣,且和我之前的工作似乎有一点点的关联,需要仔细研究下
The smallest eigenvectors of the graph Laplacian are well-known to provide a succinct representation of the geometry of a weighted graph. In reinforcement learning (RL), where the weighted graph may be interpreted as the state transition process induced by a behavior policy acting on the environment, approximating the eigenvectors of the Laplacian provides a promising approach to state representation learning.
所有审稿人中,审稿人2起初的意见相对比较negative,质疑主要围绕两点展开:
- 作者只使用random policy来学习state representation,这在比较大的MDP上显然不能对state space进行有效的探索
- 作者在文中指出,Laplacian representation的一个应用在于reward-shaping,但审稿人对sample efficiency提出了质疑,认为文章中的实验并没有公正地反映出sample efficiency
经过rebuttal审稿人接受了作者的说法
Marginal Policy Gradients: A Unified Family of Estimators for Bounded Action Spaces with Applications
With the marginal policy gradients family of estimators we present a unified analysis of the variance reduction properties of APG and CAPG; our results provide a stronger guarantee than existing analyses for CAPG.
又是来自Tencent AILab大佬Han Liu组的paper,研究的是在RTS游戏背景下的policy gradient方差问题,RTS游戏中action space往往由几个连续的变量来表示,连续变量的值往往表示英雄移动的方向或施放技能的方向等。此前RL方面还没有类似的研究RTS特定背景的的工作,值得一读。
Soft Q-Learning with Mutual-Information Regularization
Soft Q-learning的思路来源于概率图模型,之前的研究表明soft Q-learning中的entropy regularizer可以很有效地提高exploration的效率与policy的robustness,因此被广泛应用在很多RL任务中。而根据作者在abstract中的claim:
However, entropy regularization might be undesirable when actions have significantly different importance.
We propose a theoretically motivated framework that dynamically weights the importance of actions by using the mutual-information.
This regularizer encourages the policy to be close to a non-uniform distribution that assigns higher probability mass to more important actions.
文章的formulation看起来还是很漂亮的,可以仔细研究下。
Deep reinforcement learning with relational inductive biases
划重点,文章在星际2的几个小型任务上刷到了SOTA
We introduce an approach for augmenting model-free deep reinforcement learning agents with a mechanism for relational reasoning over structured representations, which improves performance, learning efficiency, generalization, and interpretability. Our architecture encodes an image as a set of vectors, and applies an iterative message-passing procedure to discover and reason about relevant entities and relations in a scene.
Preferences Implicit in the State of the World
Pieter Abbeel组的第二篇文章,文章的主旨可以用一句话概括:
Inferring preferences from the initial state of an environment.
文章中放出的代码地址https://github.com/HumanCompatibleAI/rlsp
Multi-agent RL
M^3RL: Mind-aware Multi-agent Management Reinforcement Learning
Multi-agent的工作,mark一下,有时间可以仔细看看
Learning to Schedule Communication in Multi-agent Reinforcement Learning
In this paper, we study a practical scenario when (i) the communication bandwidth is limited and (ii) the agents share the communication medium so that only a restricted number of agents are able to simultaneously use the medium, as in the state-of-the-art wireless networking standards.
Multi-Agent Dual Learning
将dual learning的思路与multi-agent结合,传统的dual learning一般是两个模型互相利用对方的对偶性质来进行学习,这篇文章将idea拓展至multi-agent环境下的多个目标之间的互相交互,并且在machine translation任务上刷到了SOTA。
Metareview:
A paper that studies two tasks: machine translation and image translation. The authors propose a new multi-agent dual learning technique that takes advantage of the symmetry of the problem. The empirical gains over a competitive baseline are quite solid.